#
2D CAD
2D CAD is a program for computer aided pattern construction and grading of garments in 2D.
Assyst.CAD is Assyst’s 2D CAD software for pattern construction and grading. To optimize pattern-based grading, smart.texture can be used to realistically display and edit fabric textures in the background
3D fashion design
3D fashion design, also known as 3D apparel design, is the computer-aided 3D visualization of a pattern on an avatar and the rendering of textures in 3D.
3D digitization
3D digitization covers the process from scanning people for 3D avatars to the finished visualization of 3D models.
3D pattern
Common terms are also 3D design, 3D cut or 3D piece. A 3D pattern refers to the three-dimensional, virtual pieces of a model for the 3D simulation of garments.
With Assyst.CAD and Style3D Studio, you can develop apparel products right through to production, saving on samples and costs.
3D rendering
After texturing and illuminating the scene with light setups, 3D rendering automatically generates photorealistic 2D images from 3D models or movements in real time through sequences of images.
3D simulation
The 3D simulation visualizes the garment, the fit and the physical properties of fabrics and accessories during the virtual fitting.
3D visualization
3D visualization is a process of various steps to create three-dimensional models with textures and illumination from two-dimensional models, resulting in photorealistic images and sequences of images.
3D/2D.Connect
3D/2D.Connect refers to the direct data exchange and synchronization of data between Assyst and Style3D in real time for a continuous design process.
With Style3D|Assyst, you can quickly apply changes from 2D to 3D or vice versa.
A
Automated marker making
Automated marker making involves the automatic nesting of pieces according to cutting specifications.
Automarker.com is a web-based service platform from Assyst for the automated laying and management of markers, marker conversion and data exchange with partners. Combined with Autocost for material optimization of orders, it enables optimal production preparation and material savings.
Avatar
Also known as a virtual body. An avatar is a 3D model used for virtual fitting and fit control in the 3D simulation.
B
Bell skirt
A bell skirt is a skirt made of several circular split pieces that are sewn smoothly at the waist and widen towards the hem. The bell effect is determined by the choice of material.
Assyst.CAD offers a quick and automated solution for the construction of a circle skirt using feature macros.

Bell sleeves
A bell sleeve, also known as a trumpet or flounce sleeve, is a flared sleeve constructed as a full circle and sewn directly from the shoulder. It gives a special character to blouses, dresses, and shirts.
Assyst.CAD offers a quick and automated solution for the construction of bell sleeves using feature macros.

Bump lines
In Assyst, bump lines are horizontal, vertical or diagonal lines across the entire marker. Pieces can be bumped and slid to a bump line. Bump lines allow you to work around defects in marker fabric, to leave a space to cut through in a very long marker, or to align pieces in an exact line. Bump lines, their position and text can be plotted.
C
Circle skirt
A circle skirt is a skirt made from a circular piece with a large hemline so that the skirt swings beautifully. A circle skirt can be symmetrical or asymmetrical.
Assyst.CAD offers a quick and automated solution for the construction of a circle skirt using feature macros.
Image: Asymmetric circle skirt

Collection
Also referred to as a fashion collection or collection development.
A collection is the selection and compilation of styles around a fashion theme for a season. While it used to take months to develop a collection, 3D simulation combined with AI speeds up the process.
With Style3D AI, you can create high-quality photo shoots and save time and money. This can also be done with your reference model or digital models that can be customized for different markets and segments, such as hair and skin color or age.
Collection framework plan
A Collection Framework Plan (CFP), also known as a collection process, is usually derived directly from the business objectives and includes the planning of the chronological and cross-departmental process from material disposition to trade show presentation and subsequent sales.
It contains all the information for each department involved in the collection creation. Updating and adapting the collection framework plan to new circumstances is an ongoing process until the collection is delivered to the sales department on time.
Custom-made
Custom-made is also known to many as tailor-made or made-to-measure. Custom-made refers to the production of garments based on an existing model that is adapted to individual measurements and industrially manufactured.
Assyst offers the Assyst.MTM add-on for custom-made production.
D
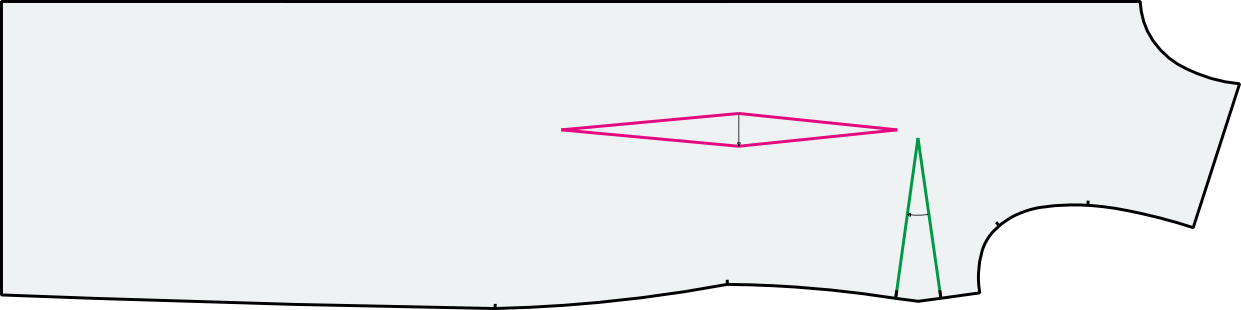
Darts
A dart is a wedge-shaped or diamond-shaped incision in a piece that shapes the area and improves the body fit. However, it can also be used as a design element. A distinction is made between contour darts and inner darts.
The image shows a contour dart at the bust and inner dart at the waist.
Displacement map
A displacement map shifts the geometry of three-dimensional surfaces, giving objects more depth and detail.
Image: The displacement map adds detail to the knit texture.

Dress size
Also known as clothing size or garment size.
A dress size is a measurement that describes the fit of a garment. It is based on certain body measurements (chest, waist and hip circumference) plus the comfort allowance. Dress sizes are only guidelines for finding the right size, but the fit may vary from garment to garment.
F
Fabric simulation
Fabric simulation is the virtual simulation of garments with fabric properties and their behavior in different situations. This includes drape, fall and movement. It gives designers and pattern makers a realistic idea of how a fabric will behave and how patterns will look on a garment.
Fitting
The fitting is a quality control. It verifies that the garment fits correctly and is comfortable. The properties of the fabrics are also taken into account. If the garment fits perfectly, it can be produced in larger quantities.
Fusing block
A fusing block combines all pieces of a garment to be fused into one block with allowances and is placed in the marker. After rough cutting, the fabric is fixed with interlining and the pieces are cut individually.
Assyst.LAY and Assyst.Automarker can manually or automatically define fusing blocks during marker making and place them to save fabric.
G
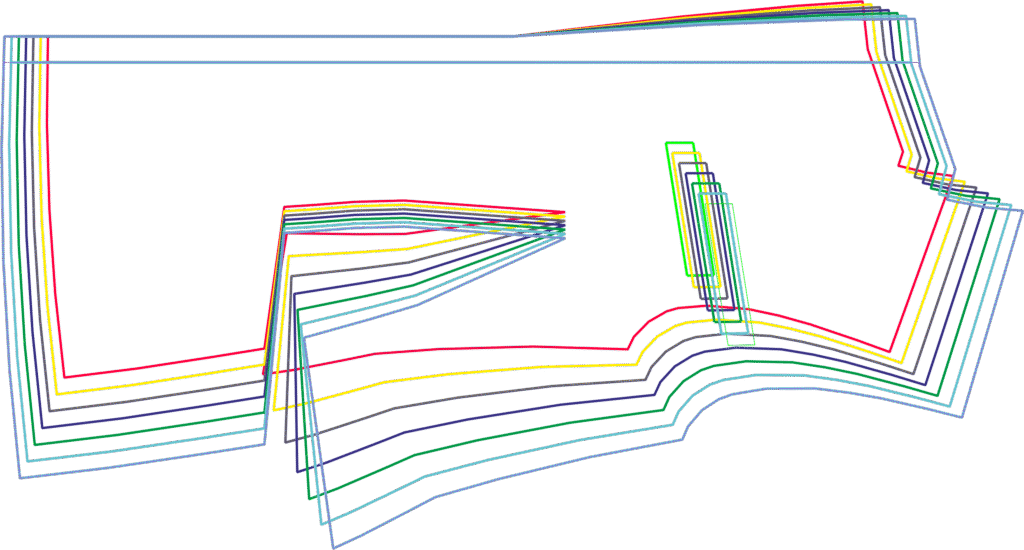
Grade nest
In a grade nest, all sizes of a piece are displayed one inside the other. In this way, you can check whether the grading is correct and make changes if necessary.
To compare certain sizes, the sizes can be selected in Assyst.CAD.
Image: Example of a grade nest
Grade rule
A grade rule defines the shift of a grade point in X and Y direction. It contains the grade rules for the next larger or smaller size.
ASSYST.CAD works with two types of grade rules, general grade rules and local grade rules.
General grade rules
General grade rules are the regular rules that are created and saved in rule tables. They are shown as positive numbers. General grade rules can be created and copied in several ways. You can also turn general grade rules into local grade rules and vice versa.
Local grade rules
Local grade rules are indicated by a minus sign (-). Unlike general grade rules, local grade rules are not stored in a rule table. They are in the rule table -1 during the current session and are saved with the respective piece. They are useful, for example, for a one-time, irregular grade that is not to be stored in the general rule table.
Grading
Grading is the adjustment of a pattern to larger or smaller sizes using grade rules. When creating a garment, a pattern is first created in the sample size, also known as the initial size. Grading uses grade rules to enlarge or reduce the pattern from this size to fit the different sizes.
The grade rules are derived from a grade point in the positive or negative X and Y directions. The calculation formulas differ depending on the size system, whether grading is manual or computer aided (CAD), and which system is used.
Grading trousers by grade rules
By taking serial measurements in different countries, standardized size tables are created based on average body sizes and proportions typical for each country. This enables the apparel industry to offer garments with the right measurements for each country. This ensures the quality and fit of the garment. Examples of these standard sizes are SIZE GERMANY, SIZE ITALY, SIZE NETHERLANDS and SIZE USA.
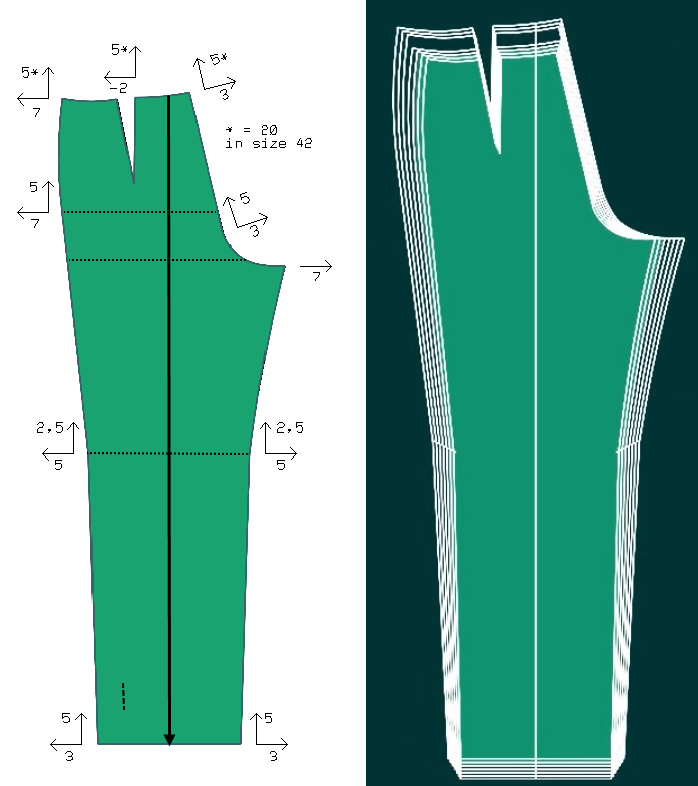
Grading value
A grading value is the dimensional difference between two sizes at a certain point on the pattern piece.
In Assyst.CAD, the grading values are stored in a rule table with numbered grade rules. The rule table can contain several size groups.
Image: Grade rules for trousers
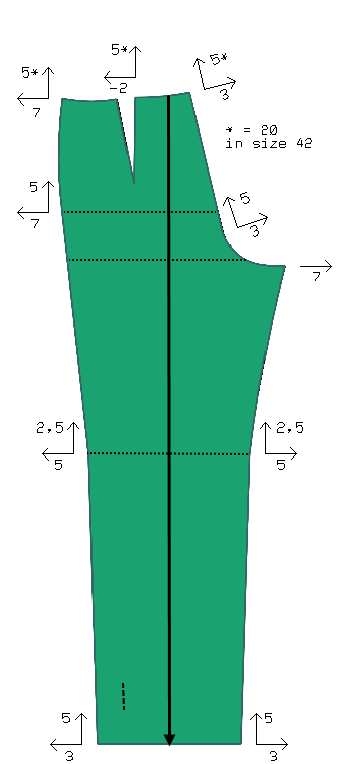
Grain line
The grain line shows the direction in which the warp threads run in the fabric. It is marked on the pattern pieces with a line and an arrow. This way, you know how to align the pieces with the fabric when cutting.
You will not find the term grain line in Assyst; instead, the generic term stripe line is used, which combines the grain line and the repeat lines.
I
Interlining
Interlining is a fabric made of different fibers that is partially ironed on, sewn on, or simply placed in between. It provides support in fixed areas, prevents the fabric from stretching, and reinforces the shell fabric in certain areas.
Also known as iron-on interlining, non-woven interlining, or fusible interlining.
M
Macro
A macro contains a series of actions that are performed automatically after a selection or click. This allows recurring processes to be carried out quickly.
Assyst.CAD provides smart.run macros that simplify and shorten repetitive design tasks. Individual macros can be programmed using smart.pattern.
Marker
The pieces are nested in a marker with the lowest possible material consumption and cutting loss for cutting. The grain lines or strip lines are decisive for the orientation of the pieces, the line direction and the matching to fabric patterns. Markers can be laid manually or automatically.
Marker making
Marker making is the process of manually or automatically placing pieces in a marker to save space. Marker making is a step in the apparel manufacturing process.
Assyst.LAY and Assyst.Automarker are nesting programs for the manual or automated laying of high-quality markers according to your specifications using individual laying rules.
N
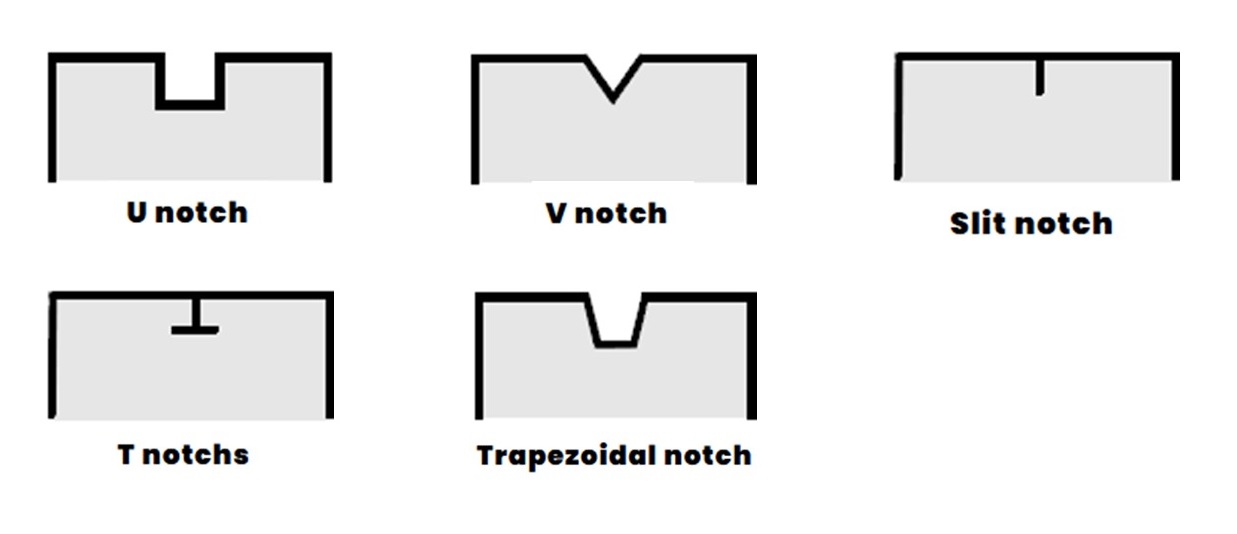
Notch
Notches (also: clip, snaps) are incisions that are used as a marking aid for sewing pieces together or for the seam width. Other examples: Pleat, dart position, front sleeve…
In Assyst.CAD, all notches are defined by base width, end width, length, and angle.
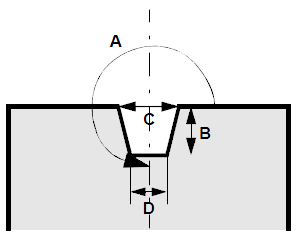
Notch grading is a special topic
When it comes to notch grading, Assyst.CAD provides a feature, notch coding, which makes it easy to grade notches correctly without any additional grading value.
Image: Notch types and shapes
P
Pattern
Common terms include cut, template, 2D pattern.
A pattern refers to all the pieces of a model that are used as a template for cutting. If the pattern is graded, it contains all sizes.
One example is the well-known sewing patterns for domestic use; in industry, patterns look like the image on the right.
With Assyst.CAD, you can quickly and effectively create and grade patterns for your collection.
Image: Example of a women’s garment pattern for shell fabric in size 38
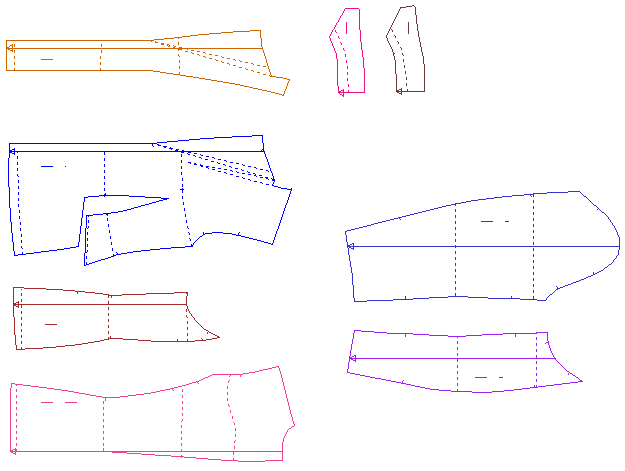
Pattern construction
Pattern construction is the construction of patterns in 2D for cutting.
Assyst.CAD is one of the market-leading CAD systems for pattern construction.
Piece
A piece is also referred to as a cut piece, pattern piece or 2D piece.
Pattern pieces are the created pieces of a pattern that will be used to cut the fabric. Sewn together, they make the finished garment.
In Assyst, we refer to them simply as ‘pieces’. In the 3D world, we distinguish between created 2D pieces and virtual 3D pieces for simulation.
Pleate
For a pleat, a certain area of a fabric is placed on top of or against each other, depending on the type. The most common types of pleats are the knife pleat, the box pleat or the crease pleat. The processing of a pleat also plays a role: pleats can retain width or add width by popping open. A well-known example is the pleated skirt.
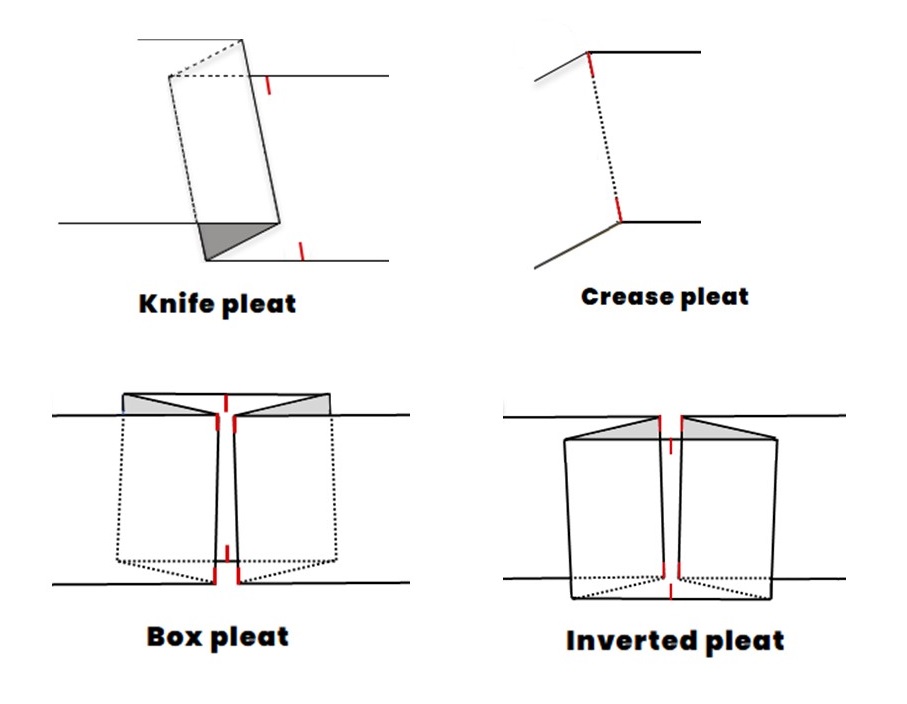
Q
Quilling
A quilling or flounce is a circular cut piece with a large hemline. It is sewn on smoothly and has a flowing, soft fall due to the circumference of the hem. Quilling is used on sleeves, hems, shoulders, and collars.
Assyst.CAD offers a quick and automated solution for the construction of quilling using feature macros.
Image: Half sleeve with quilling

R
Raytracing
Raytracing is a rendering technique used to make images look as realistic as possible. Light setups are used to create realistic lighting, shadows, and reflections on 3D models. In combination with AI (Artificial Intelligence), realistic images can be rendered even faster and more efficiently
Style3D AI enables yout to create high-quality photo shoots with your reference model or digital models. It is also possible to adjust hair and skin color or age.
Ruffle
A ruffle is a quilling or spiral flounce with extra length, which is maintained and gathered when sewn on to create the ruffle effect.
In Assyst.CAD, you can create ruffles quickly and easily using smart.run macros.
Image: Ruffle at the hemline

S
Sample collection
A sample collection is a prototype or sample piece developed by the designer to showcase the designs and fits of a new collection. It serves as an inspiration to get feedback and make changes before final production begins.
With Style3D AI, you can automatically create fabric patterns and collection designs and present your ideas with the AI Try-on on the model.
Sample size
Also referred to as base size or pattern size.
The sample size is the size in which a pattern is created. From this size, the smaller and larger sizes are derived step by step using grade rules.
Seam
Other common terms include stitching, seam contour, suture, or connection.
A seam joins pieces of a garment to give them shape and fit. There are different types of seams that are used depending on the purpose and design, such as flatlock, blindstitch, overlock, zigzag and many more. The seam is important to the durability and appearance of the garment.
Size chart
Other common terms are size table, size guide and measurement chart.
A size chart contains the measurements for each size of various ready-to-wear garments (women’s, men’s, children’s). It is based on measurements such as chest, waist, hip, and height. It is used as a guide to find the right size and ensure the fit of a product.
Size range
A size range contains all sizes of a model created by the grading.
If only selected sizes are to appear in the work area, special size ranges can be defined in Assyst.CAD. This makes it possible to work clearly on specific sizes.
Spiral flounce
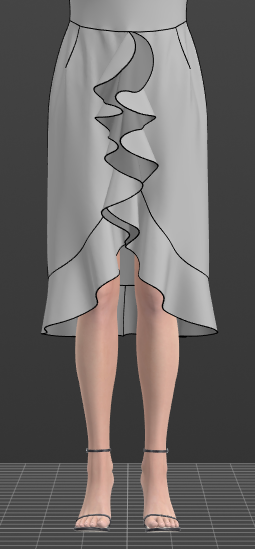
A spiral flounce is a piece designed as a spiral, primarily for necklines, with optimal fabric usage. The waves are evenly increasing or decreasing Either eye-catching and eccentric or girly and romantic, depending on the draping and styling.
Image: Spiral flounces on the skirt hem
T
Texture mapping
Texture mapping involves projecting textures onto 3D models for the realistic display of fabrics/surfaces for 3D rendering.